How Can You Organize Things Into Categories of the Same Type Language Arts

WHAT IS A PROCEDURAL TEXT?

A procedural text instructs your audience on how to complete a specific job. Generally, this then falls into two categories, how to brand something and how to do something.
The purpose of a procedural text is to provide sequenced information or directions so that people tin successfully perform activities in safe, efficient and appropriate ways.
You may see procedural writing also referred to equally a PROCESS ANALYSIS ESSAY in some parts of the world. This championship provides students with a greater agreement of their purpose of analyzing a process and writing it upwardly equally a unproblematic PROCEDURE to be followed by the reader.
Recipes and science experiments are common examples of procedural texts. They apply headings and sub-headings that can be structured in the following manner.
Some common forms of procedural texts are.
- Directions – How do I go somewhere? Very specific instructions including location names and titles. Formal language is required and the improver of a map will make your instructions so much easier to empathize.
- Instructions – How do I do something? Your language must see the needs of your audition and you may need to include a diagram if at that place are complex elements to complete.
- Recipes – How do I cook something? Recipes are a universal text. There is a very articulate expectation of the audience so never devious from the essentials. Ingredients, method and a few visuals are essential.
- Rules for games – How do I play this? Be witting of your audience and write in a style and language they will sympathise. You are virtually guaranteed to require visuals in this way of writing.
- Manuals – How do I operate this? Are there whatsoever warnings I need to be enlightened of earlier proceeding? Be very specific in your explanation.
- Agendas – What are we doing? When are we doing it? Who is responsible?
It is clear that having a good grasp of this type of genre writing has multiple possible existent-life applications for our students. Luckily for such an of import genre, procedural texts are one of the easier genres to teach and to successfully produce as a student.
Every bit a comparatively straightforward nonfiction genre, procedural texts in their many forms are often easier to grasp for those students who don't possess a natural affinity for writing than some of the more than creative writing genres. The learning of a series of criteria will ensure that even weaker students can produce coherent and successful procedural texts.
A Complete Unit ON PROCEDURAL TEXTS

This HUGE Parcel offers 97 PAGES of hands-on, printable, and digital media resource. Your students will exist WRITING procedures with STRUCTURE, INSIGHT AND Noesis like never before.
PROCEDURAL AND Explanation TEXTS – WHAT'S THE Deviation?

An explanation text is similar to a procedural text and these can often be dislocated, however, a procedural text explains the how and why backside a process such as
- What causes a Tsunami?
- Why are our pelting forests disappearing?
- The process of making aluminum.
A procedure generally instructs the audience how to make or do something, such as a recipe. Although they have similarities they are two very singled-out writing tasks.
Read our guide on how to write an explanation text here.
PROCEDURAL TEXT STRUCTURE
HEADINGS Titles bespeak the goal or aim of your procedure.
SECTIONS Keep everything organised and in lodge.
SUBHEADINGS Subheadings such every bit materials, what to practice next, warnings indicate the stages of the procedure.
SEQUENCE Everything is organized in the sequence it is to occur and each new step must begin on a new line.
PROCEDURAL TEXT FEATURES
VOCABULARY Use technical and specialized terms in a procedural text. Don't impaired things down.
TENSE Always write in timeless present tense
FLOW Use connectives and conjunctions related to time to indicate the chronological order of the deportment.
DETAILS Details are important in a process. Presume very trivial.
VISUALS Greatly enhance a procedural text and reinforce technical instructions. Maps, diagrams and photos are essential.
HOW TO WRITE A GREAT Procedure VIDEO TUTORIAL (4:30 mins)
THE FOUR MAIN COMPONENTS OF A PROCEDURAL TEXT
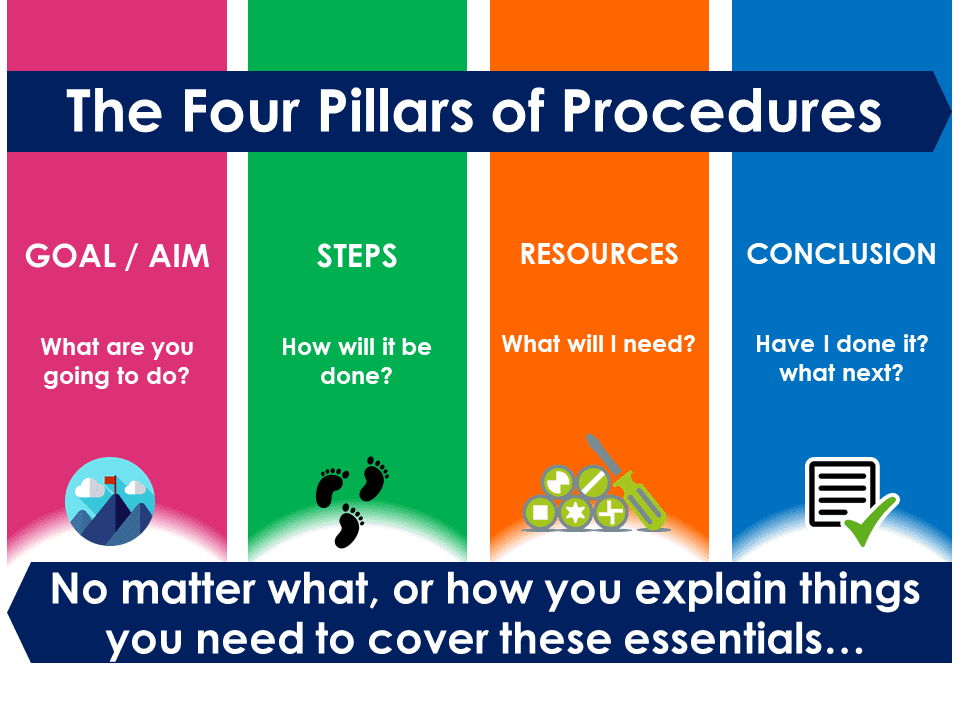
Let's have a expect at the four main sections that course a procedural text to ensure our students get a broad overview. Then, we tin accept a closer look at some of the finer details.
1. Goal / Aim
This component addresses the what of the piece. It will refer to what is to be done or made. Very frequently too this volition provide for the title of the text itself. Oft this volition exist stated in the class of a 'how to' sentence or the name of the matter to be made itself. With more than technical procedural texts, titles may be more generic and standardized, such as but Operating Transmission or User's Guide or in its most basic form, Instructions.
To assistance your students get a sense of the importance of the title and its relationship with the goal of the text, provide them with a ready of procedural texts with the titles removed. In groups, have them brainstorm a multifariousness of titles for the text. When they are finished, reveal the original title of the text and compare information technology with the suggestions made by the group. Shortly they will get-go to run into the pattern evolve and this volition assist them when they come up to produce and name their own procedural texts.
ii. Resources
Commonly done in the grade of a listing, this component may also be titled Materials, Equipment, Ingredients, Items Needed etc and is pretty self-explanatory. This component comprises a listing of things required to complete the process outlined in the text. For a recipe, this volition evidently include things similar ingredients, but may besides include things similar the appliances and tools required to follow that recipe to completion. For flat-pack furniture, for example, items like a screwdriver, spanner, the mucilage will form this section. Science experiment procedural texts volition include apparatus such equally Bunsen burners, test tubes, litmus paper etc. Regardless of the specific purpose of the text in question, the resources listed in this section volition unremarkably be presented in the order they will be used, every bit far as this is relevant or possible.
3. Steps
This is the centre of the procedural text equally it outlines stride-by-step the methodology to follow in the process itself. Again, the title of this section of the procedural text may vary depending on the specific type of writing information technology is. Longer user guides and instructional manuals will have a circuitous and extensive list of steps to follow that will employ subtitles and subsections to explain micro-processes inside the wider procedure being described. Simpler texts, such as recipes, will be much less complex in structure. It is important to encourage students to retrieve very logically about the process they are attempting to outline in their writing. Too oftentimes students write themselves into corners as they try to describe complicated procedures while struggling with the technical difficulties of amalgam grammatically sound sentences. A expert rule of thumb for student writers is to use many short and simple sentences when writing nigh complex ideas. We will talk more on this aspect when we talk over linguistic communication features in greater particular.
4. Conclusion
The conclusion of a procedural text offers guidance to the reader on how they can evaluate the success of the process that has been followed. This may accept the form of, for example, a description of the completed meal for a recipe text or a description of the assembled piece of furniture in a flat-pack didactics guide. Depending on the type of text in question, often illustrations tin be used to reinforce what a successfully followed process volition look similar.
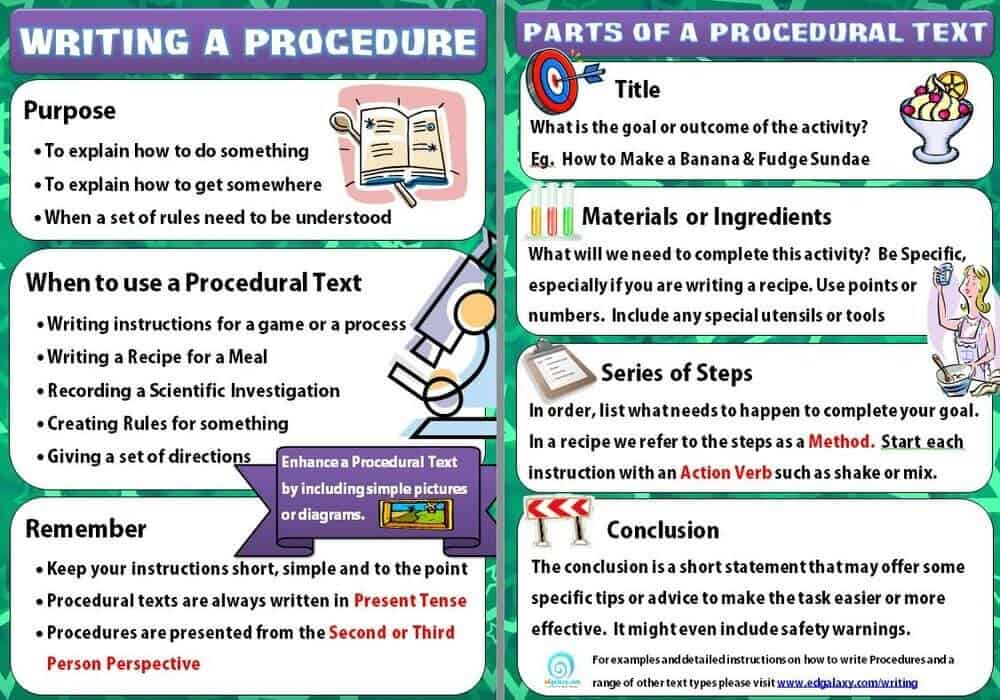
Language FEATURES OF A PROCEDURAL TEXT
Given the broad range of forms, a procedural text may accept, we should not expect that all of the structure and features outlined will apply equally to each blazon of text. However, the following is some valuable general advice for students to bear in mind when they are considering the language registers of their text.
Procedural texts are i of the few writing genres that regularly use the second person pronoun that addresses the reader in a general way. Often also, this 'you' volition be unsaid through the apply of imperatives at, or near, the first of sentences.
Given the nature of these types of text, the simple present tense is the preferred tense for this type of writing. In this regard, information technology offers a corking opportunity to focus on verb work, particularly on imperatives. These control words, or bossy words, such equally cut, accept, hold are often used to requite orders for readers to follow as they motion step by footstep through the process outlined in the text.
This is a nonfiction genre and this should be reflected in the choice of language. There is little to no place here for flights of imagination or figurative turns of phrase. Students should stick to plain, straightforward sentence structures and word choices. They should include detailed factual descriptions of things, where this volition heighten the reader's understanding; shape, size, color, amount should be included where it will improve this understanding.
Sentences should also provide detailed information on the how of performing each of the steps in the process outlined. For example, remove advisedly rather than simply remove – when intendance is necessary for satisfactory functioning make sure it is stated explicitly.
Actions should exist outlined sequentially and time connectives can be used to help organize the necessary steps chronologically. For example, use of adverbial time words, such as: first, second, before, then, after. Encourage students to focus on answering the questions of where and when of each of the actions they instruct the reader to follow.
POINTS TO CONSIDER BEFORE "PROCEEDING"
- What is to be done or fabricated? What is the aim or goal? What might your title exist?
- What is needed to consummate this? Materials, ingredients, tools and so on.
- In what order should things exist done? What are the steps in the process? What is the all-time mode to organize and present them?
- What will yous add to your written text to assistance the audience sympathise better? ( diagrams, illustrations, pictures etc. )
USE HEADINGS TO KEEP YOUR READERS ON Runway
Recipe – Sub Headings (Instance)
- Ingredients
- Method
- Serving Suggestions
Science Report – Sub Headings (Example)
- Aim / Hypothesis
- Appliance
- Method; Results
- Conclusion
THINK LOGICALLY AND Assume VERY Piddling.
The challenge in writing a skilful procedural text is to deliver your instructions in a logical fashion. Ensure your instructions are straight to the point and that you as the author sympathize what you lot are trying to achieve. You really want to reply three questions to your audition.
- What volition I need to consummate this task?
- What do I have to do to consummate this task?
- How will I know if I completed the task correctly?
Ensure you also conspicuously empathize your audience, equally this will have a big impact upon the linguistic communication you use.
ILLUSTRATIONS: PICTURES PAINT A THOUSAND WORDS
It tin often be hard to draw actions in words – even for accomplished writers. Casting a quick center over the sports pages of the newspaper will quickly reveal the importance of the visual in relaying information. You lot'll notice photographs that convey the delivery and cede of the athlete to their sport far meliorate than most of us are capable of conveying with our meagre linguistic communication skills. The old newsman's adage A picture paints a thousand words tin can be just as true for procedural texts. But photographs aren't the merely visual means of reinforcing the written give-and-take in procedural texts. Students can, depending on the nature of the text, employ diagrams, schematics, tables, even cartoons! As with the written text, these images will often be ordered sequentially forth with the corresponding text and volition usually be labelled or accompanied by a caption.
But What to Write Virtually?
One of the things that make procedural texts an accessible writing genre for our students is one of the things that tin can besides get in an uninspiring genre for students to appoint in, that is, its factual, straightforward nature. There is a reason why we don't sit upwardly all night reading user manuals! Entertaining the reader is non the priority of a procedural text and information technology shows.

So how can we spark the involvement of our students strong enough to carry them through the procedure of producing a completed text? I style is to become artistic with the titles of the procedural texts nosotros enquire them to produce. For instance, if we are teaching recipe writing your students may be marginally less than thrilled to be tasked with writing a recipe on 'How to Make Scrambled Eggs'. Why not add a nuance of imagination to it? How about, 'How to Brand the Nearly Disgusting Sandwich in the Globe' – at present, isn't that a niggling more interesting? Sure, no one will actually make the stop production – who wants a toenail clipping sandwich garnished in boogers anyways? But, the educatee will yet have to organize their text to the same structures outlined to a higher place. They will have to consider the aforementioned language features and measure the success, or otherwise, of their writing to the same criteria of a more deadpan procedural text topic.
Another way to ensure pupil engagement in the writing of procedural texts is to set them a topic that appeals to their own interests specifically. It may exist a sporting interest – How to Take a Penalisation Boot, a musical 1 – How to Melody a Guitar or an arts and crafts based chore – How to Make a Paper Aeroplane. All that is needed is a topic that interests the student and one that they have a sure competency in.
Even if the student chooses something they practise not have competency in, and if it isn't likewise complicated, they may wish to take the learning opportunity and research something new with a view to writing a procedural text based on what they learn. This tin be smashing for longer-term projects and tin also be linked to things they have learned in other subjects at school. Reconstructing their learning in this mode offers a wealth of subconscious assessment opportunities for the teacher, providing valuable information to inform future planning and provide data for recording and reporting.
PROCEDURAL TEXT SUCCESS CRITERIA AND Cess
Early in this guide, we outlined the four master components of a procedural text, the concluding of which was the conclusion. The determination, we stated, "offers guidance to the reader on how they tin evaluate the success of the procedure that has been followed." Too, in teaching our students to produce procedural texts we must offering them a means to assess whether or non they take completed the chore successfully themselves. 1 way they tin can achieve this is by the utilise of a Success Criteria checklist. The features students are required to include tin can be listed in a column to the left and in the right-manus column, students can check if they accept the feature, or quote an example as evidence from their text itself. For example:

For students to successfully produce their own pieces of genre writing they must internalize the features of that writing genre. To do this they must be exposed to successful and unsuccessful examples of the genre to develop a skilful critical sense. Peer cess is a good means of achieving this. Have your students commutation their work with each other and, using a template similar to the example above, they can assess each other'southward work. This is a peachy method to give your students the practice required to internalize the criteria for successful procedural writing. Varying the number and the complexity of the items on the criteria checklist is a convenient means of catering to different ages and abilities too.
The Proof is in the Pudding
A more than practical means of assessing the effectiveness of a procedural text is for students to bandy their writing with 1 another and then deport out the instructions in their classmate'south text to the letter. If they tin can correctly perform the job exclusively in response to these written instructions, then the writing has been, at least on a purely practical level, successful. Of form, this method does not account for a lot of technical elements that the teacher will still demand to check for, just it can be a lot of fun and an opportunity for the students to share their cognition and interests with 1 some other.
If At First, You Don't Succeed…
As I stated previously in this commodity, procedural texts are one of the more than straightforward writing genres for students to primary. That said, however, mastery simply comes with focused practice. Though structurally this genre is fairly easy for students to grasp, at that place are still a lot of linguistic communication features to consider and stylistic conventions to attach to. As well as that, there is considerable variety in the complication of the diverse types of procedural texts; from simple recipes all the way to complex user manuals. All this takes considerable practice, then it is important that students are offered regular opportunities to hone the broad range of skills required to write well. Some of this learning will take identify in detached sessions dedicated to the writing of procedural texts, but many of the skills will be adult while working on general language skills, whether focused on verbs, tenses, punctuation, reading etc it will exist useful to make links to principles in common with the various writing genres equally and when they arise.
TIPS FOR WRITING A Slap-up PROCEDURAL Written report
Didactics Resources
Utilise the resources and tools below with your students to improve their writing skills through proven didactics strategies.
PROCEDURAL TEXT GRAPHIC ORGANIZER TEMPLATE

Procedural text Example (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of procedural texts. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater item. Please take a moment to both read the procedures in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the key elements of writing a process earlier first.
Please empathize these pupil writing samples are not intended to exist perfect examples for each age or course level simply a slice of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of procedural text writing.
Nosotros would recommend reading the example either a year above and below, as well as the grade y'all are currently working with to gain a broader appreciation of this text blazon.
PROCEDURAL WRITING CHECKLISTS
A COMPLETE Unit of measurement OF Work ON PROCEDURAL TEXTS?

We pride ourselves on beingness the spider web's all-time resource for teaching students and teachers how to write a swell procedure and value the fact you take taken the fourth dimension to read our comprehensive guides to understand the fundamentals of writing a sequence of actions or events.
Nosotros also understand some of you don't have the luxury of time or the resources to create actually engaging resource when yous need them.
If you are time-poor and looking for an in-depth solution that encompasses all of the concepts outlined in this article, I strongly recommend taking a look at the Perfect Procedural Writing Unit.
Working in partnership aslope Innovative Didactics Ideas, we confidently recommend this resource equally an all in one solution to teach procedural writing.
Inside this unit, y'all will notice over seventy pages of engaging and innovative teaching ideas.
OTHER Dandy ARTICLES RELATED TO PROCEDURAL TEXTS
The content for this folio has been written by Shane Mac Donnchaidh. A former principal of an international school and university English lecturer with fifteen years of teaching and administration experience. Shane'southward latest Book the Consummate Guide to Nonfiction Writing tin exist plant here. Editing and back up for this article have been provided by the literacyideas team.
Source: https://literacyideas.com/procedural-texts/





0 Response to "How Can You Organize Things Into Categories of the Same Type Language Arts"
Postar um comentário